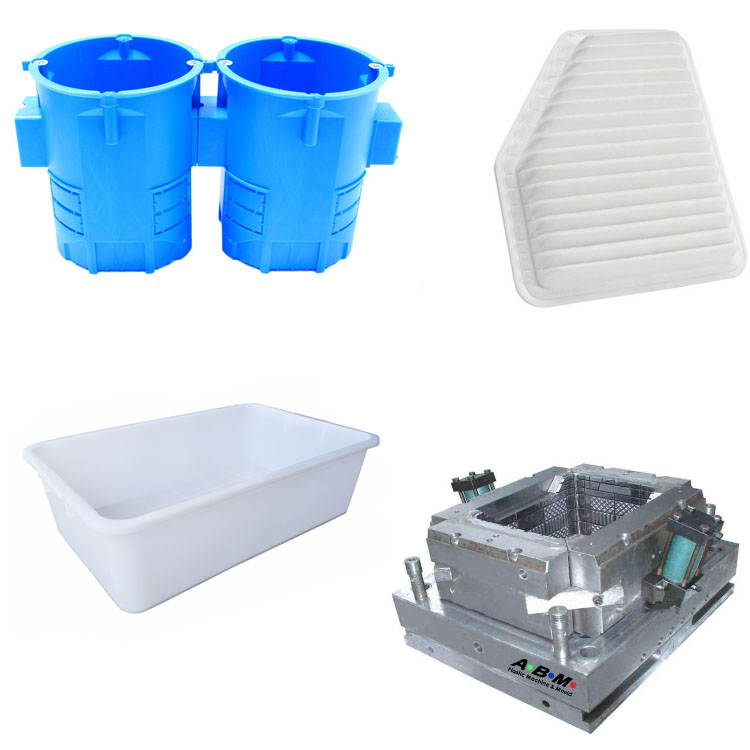
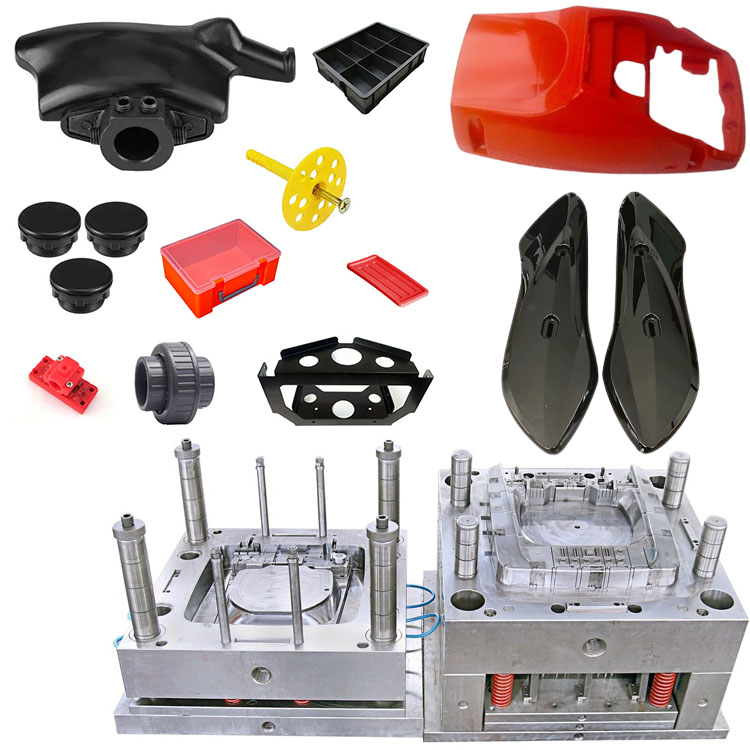
- Core Customization Service
- Health Care
- Electronic Appliances and Instruments
- Maternal and Child Supplies Molds
- Recreational Sports
- Home Furnishing Art
- Auto Accessories
- Transportation and Warehousing
- Lighting Fixtures
- Construction Equipment
- Packaging Product
- Educational & Laboratories
- Clothing Luggage Accessories
- Care and Cleaning Products
- Agriculture & Forestry
- Mechanical Equipment
- Pet Supplies
- Kitchenware
China Custom Molding Manufacturer, Supplier, Factory
Custom molding includes: injection molding, blow molding, die casting and rotational molding. We have 17 years of experience in these molding technologies.
Injection molding
Injection molding is a manufacturing process that injects molten plastic into the mold cavity and forms a product after cooling and solidification. Its core principle is to use the screw or plunger of the injection molding machine to heat the plastic raw material to a molten state, and then inject it into the closed mold at high pressure to finally obtain a plastic part that is consistent with the mold structure.
1. Process flow
Mold closing: The mold is closed to form a closed cavity.
Injection: The molten plastic is injected into the mold at high speed through the nozzle.
Pressure holding: Continuous pressure is applied to compensate for material shrinkage and ensure the shape is complete.
Cooling: The product is cooled and shaped in the mold, and the time depends on the material properties and wall thickness.
Mold opening and part removal: The mold is opened and the ejector mechanism pushes the finished product out
2. Main application areas
Medical equipment: Production of high-precision parts such as microscope housings, medical containers, etc., which must meet sterility and corrosion resistance requirements.
Consumer electronics: Manufacturing of precision parts such as mobile phone cases and connectors.
Automotive industry: Instrument panels, interior trims, etc., focusing on the balance between lightweight and strength.
Packaging industry: Production of large-volume products such as bottle caps and thin-walled containers
3. Technical features
Hydraulic injection molding machine:
Advantages: low cost and adaptability to large tonnage requirements.
Weaknesses: high energy consumption (accounting for more than 60% of the total energy consumption of the equipment) and limited accuracy (±0.1mm)1.
All-electric injection molding machine:
Advantages: Energy saving of 30%-60%, accuracy of ±0.02mm, and support for multi-action synchronous operation.
Challenges: Core components (such as Japanese screws) are imported and have high maintenance costs
Blow molding:
Blow molding is a process that uses compressed air to blow the molten plastic parison to fit the mold cavity, and obtains a hollow product after cooling and shaping. It is widely used in packaging containers, industrial parts, medical equipment and other fields.
1. Basic principle
Plastic raw materials (such as PE, PP, PVC, etc.) are melted by heating to form a tubular or prefabricated parison.
The high-temperature parison is placed in the mold, and compressed air is injected to expand it to fit the inner wall of the mold. After cooling and shaping, it is demolded.
2. Typical process flow
Extrusion blow molding: extruder melts plastic → extrude tubular parison → mold clamping → blowing → cooling → demolding. Suitable for large containers (such as oil drums, storage tanks).
Injection blow molding: injection molding machine molds prefabricated parison → transfer to blow molding mold → blowing → cooling → demolding. Suitable for high-precision small products (such as medicine bottles, cosmetic bottles).
Stretch blow molding: Axial stretching of the preform before inflation (such as injection stretch blow molding) can improve material strength and transparency, and is commonly used in PET bottle production
3. Mold structure
Parting surface design: Usually parting is performed along the plane with the maximum contour of the product. Complex products can use multi-petal molds or curved surface parting to ensure smooth demolding.
Plank opening and residual material groove: When the mold is closed, the preform needs to be clamped off and the residual material needs to be accommodated. The incision angle and width affect the sealing and seam strength. It is generally designed as a 30°~60° blade structure.
Cooling system: Evenly distributed cooling water channels can shorten the molding cycle and prevent uneven shrinkage of the product. Copper alloy or beryllium copper inserts are often used to improve cooling efficiency
Die Casting
Die Casting is a casting process that injects molten metal into a precision mold cavity under high pressure and forms high-precision metal parts through rapid cooling
1. Core Principle:
High-pressure filling: The molten metal is filled at high speed under a pressure of 50-150MPa (the flow rate can reach 30-60m/s) to ensure the complete molding of complex structures.
Rapid cooling: The mold temperature is controlled at 150-300℃ to achieve microsecond solidification of the molten metal and reduce grain coarsening
2. Mold design and manufacturing
Material selection: H13 hot working die steel or 718H alloy steel is used, and the hardness must reach HRC45-501.
Structural design: It includes multi-stage cooling water channels (diameter 6-12mm) and vacuum exhaust system (vacuum degree ≤50kPa).
Processing technology: Combination of 5-axis CNC machining (accuracy ±0.01mm) and EDM (surface roughness Ra≤0.8μm
3. Material selection: Aluminum alloy (ADC12) Magnesium alloy (AZ91D) Zinc alloy (Zamak)
4. Die-casting machine type:
Cold chamber die-casting machine: Suitable for aluminum alloy/magnesium alloy (clamping force 400-4000 tons)
Hot chamber die-casting machine: Specialized in zinc/tin alloy (production efficiency up to 3000 times/shift)
Rotational molding
Rotational molding is a process that uses mold rotation and heating to make the plastic raw materials adhere evenly and form a shape. It is mainly used to produce hollow, large or complex plastic products. Its core processes include:
Mold rotation: The mold rotates along two vertical axes (revolution + rotation) to ensure that the raw materials are evenly distributed.
Hot melt curing: Heat to melt the powder or liquid plastic, and form a homogeneous product after cooling
Process flow and key technologies
1. Mold preparation
Material selection: Common mold materials are aluminum alloy or steel, which are required to be resistant to high temperature and corrosion. For example, a cast aluminum alloy mold can process an 8-meter-long kayak mold at one time.
Surface treatment: Improve surface accuracy through polishing, chrome plating or leather pattern treatment.
2. Loading and heating
Raw material feeding: Accurately measure powdered plastics (such as polyethylene), and the melt index is usually 3-6 g/10min to optimize fluidity.
Heating control: The temperature must be accurate to above the melting point of the resin to avoid bubbles.
3. Rotational molding
The mold rotates three-dimensionally in the heating furnace, and the plastic relies on gravity to evenly coat the inner wall to form a product without welds and internal stress.
4. Cooling and demolding
Forced cooling: Use water spray or ventilation to accelerate shaping, and the product automatically detaches from the mold after shrinking2.
Post-processing: Clean the mold residue and prepare for the next cycle
- View as
Phone parts customize moulding
Ningbo (P&M) Plastic Metal Products Co., Ltd. has 17 years of mold manufacturing technology and can customize phone parts customize moulding. We provide professional customized phone parts customize moulding services, and we are a professional phone parts customize moulding manufacturer. We have sufficient experience in selecting product raw materials and mold materials. In the process of customizing phone parts customize moulding, our factory can provide one-stop service. We have design and production capabilities related to phone parts customize moulding, such as: CAD design, mold manufacturing, injection molding, plastic product production, assembly and other technologies.
Read MoreSend InquiryMini car parts keychain customized moulding
Ningbo (P&M) Plastic Metal Products Co., Ltd. has 17 years of mold manufacturing technology and can customize mini car parts keychain customized moulding. We provide professional customized mini car parts keychain customized moulding services, and we are a professional mini car parts keychain customized moulding manufacturer. We have sufficient experience in selecting product raw materials and mold materials. In the process of customizing mini car parts keychain customized moulding, our factory can provide one-stop service. We have design and production capabilities related to mini car parts keychain customized moulding, such as: CAD design, mold manufacturing, injection molding, plastic product production, assembly and other technologies.
Read MoreSend InquiryCustom packaging box auto parts moulding
Ningbo (P&M) Plastic Metal Products Co., Ltd. has 17 years of mold manufacturing technology and can customize custom packaging box auto parts moulding. We provide professional customized custom packaging box auto parts moulding services, and we are a professional custom packaging box auto parts moulding manufacturer. We have sufficient experience in selecting product raw materials and mold materials. In the process of customizing custom packaging box auto parts moulding, our factory can provide one-stop service. We have design and production capabilities related to custom packaging box auto parts moulding, such as: CAD design, mold manufacturing, injection molding, plastic product production, assembly and other technologies.
Read MoreSend InquiryCustom auto parts moulding
Ningbo (P&M) Plastic Metal Products Co., Ltd. has 17 years of mold manufacturing technology and can customize custom auto parts moulding. We provide professional customized custom auto parts moulding services, and we are a professional custom auto parts moulding manufacturer. We have sufficient experience in selecting product raw materials and mold materials. In the process of customizing custom auto parts moulding, our factory can provide one-stop service. We have design and production capabilities related to custom auto parts moulding, such as: CAD design, mold manufacturing, injection molding, plastic product production, assembly and other technologies.
Read MoreSend InquiryCustom air conditioning parts for assembly moulding
Ningbo (P&M) Plastic Metal Products Co., Ltd. has 17 years of mold manufacturing technology and can customize custom air conditioning parts for assembly moulding. We provide professional customized custom air conditioning parts for assembly moulding services, and we are a professional custom air conditioning parts for assembly moulding manufacturer. We have sufficient experience in selecting product raw materials and mold materials. In the process of customizing custom air conditioning parts for assembly moulding, our factory can provide one-stop service. We have design and production capabilities related to custom air conditioning parts for assembly moulding, such as: CAD design, mold manufacturing, injection molding, plastic product production, assembly and other technologies.
Read MoreSend InquiryPlastic car parts custom moulding
Ningbo (P&M) Plastic Metal Products Co., Ltd. has 17 years of mold manufacturing technology and can customize plastic car parts custom moulding. We provide professional customized plastic car parts custom moulding services, and we are a professional plastic car parts custom moulding manufacturer. We have sufficient experience in selecting product raw materials and mold materials. In the process of customizing plastic car parts custom moulding, our factory can provide one-stop service. We have design and production capabilities related to plastic car parts custom moulding, such as: CAD design, mold manufacturing, injection molding, plastic product production, assembly and other technologies.
Read MoreSend Inquiry