Application of injection molds for motorcycle parts
2025-11-27

The application of injection molding for motorcycle parts is an extremely demanding field in terms of performance, appearance, cost, and durability. While similar to automotive injection molding, its unique characteristics stem from the motorcycle's more compact structure, greater environmental exposure, and emphasis on a seamless human-machine interface.
The following is a comprehensive analysis of the application of injection molding for motorcycle parts.
I. Application Scope: From Appearance to Core Functional Components
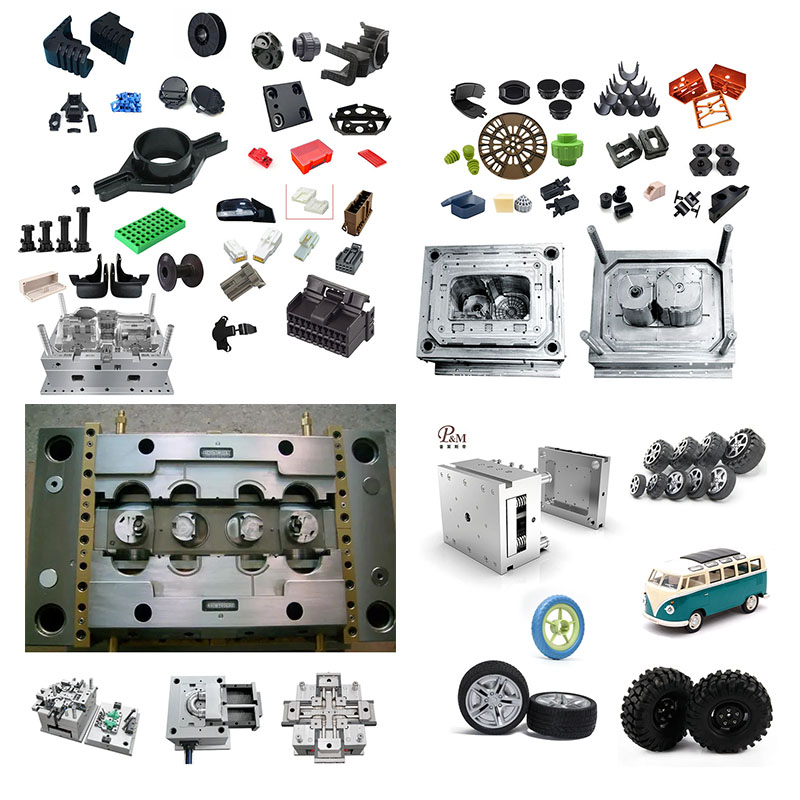
Plastic injection molded parts are ubiquitous on motorcycles, primarily falling into the following categories:
1. Exterior Coverings & Aerodynamic Systems
This is the largest and most prominent application, directly determining the motorcycle's aesthetics and aerodynamic performance.
**Full Flyes:** The outer shell of sport bikes and street bikes, featuring large, complex curved surfaces requiring extremely high surface gloss and consistency.
**Fenders:** Front and rear fenders, with a relatively simple structure but needing good toughness.
**Side Covers/Decorative Panels:** Parts covering the sides of the frame, typically bearing the brand logo.
1. **Fairing/Windshield:** May require transparent (e.g., PC material) or colored components.
2. **Functional and Structural Components:** These inconspicuous parts are crucial to the motorcycle's safety and functionality.
**Intake Manifold:** Requires high heat resistance and strength, commonly using PA66-GF30.
**Air Filter Housing:** Requires sealing and oil resistance.
**Dashboard Housing:** An aesthetic component, requiring weather resistance and UV protection.
**Handleguard Covers/Handleguard Ends:** Often made using injection molding with an internal rigid ABS frame and an external soft TPE/TPU material for a comfortable grip.
**Lamp Sockets and Housings:** Headlight and taillight housings; headlight housings may be made of transparent PC.
**Various Brackets and Mounts:** Such as rearview mirror brackets, license plate holders, etc.
3. **Engine Peripheral Components:** Operating in harsh environments, requiring high temperature and oil resistance.
**Engine Side Covers:** Replace some metal covers to achieve weight reduction.
Clutch cover
Oil sight glass: Small transparent part.
4. Interior Parts (mainly scooter)
Dashboard assembly: Integrates speedometer, tachometer, indicator lights, etc., complex structure.
Front storage compartment/glove box
Foot pedals
III. Core Manufacturing Process and Quality Control
Motorcycle part molds follow the general process of precision molds, but with different focuses:
DFM (Manufacturability Analysis): Crucial. Key analysis:
Parting line design: How to hide it in an inconspicuous location and ensure that flash does not affect the appearance.
Gate location: Must be placed on a non-visible surface or in a location that can be covered later.
Shrinkage rate: For large exterior parts, it is necessary to accurately calculate shrinkage in different directions to prevent large gaps during assembly.
Mold flow analysis: Absolutely necessary.
Predict weld line locations and guide them to low-stress or non-visible areas.
Optimize holding pressure curves to prevent shrinkage depressions on the surface of large cover parts.
Mold Steel and Machining:
High-purity steel with excellent mirror finish (such as Swedish S136 H and German 2344 ESR) is commonly used for exterior parts.
Complex curved surfaces are machined using five-axis CNC machining, corner clearing is performed using precision EDM, and inserts are machined using wire EDM.
Mold Testing and Verification:
Appearance Review: Standard parts undergo rigorous review by the customer under standard lighting conditions.
Performance Testing:
Drop Test: Simulates the drop of parts such as side covers when the vehicle is parked.
Vibration Fatigue Test: Simulates engine and road vibrations to ensure no cracking at mounting points.
Weather Resistance Test: Accelerated aging tests are conducted in a UV aging chamber.
IV. Summary: How Injection Molds Empower Modern Motorcycle Manufacturing
Achieving Sharp Shapes: Injection molding technology allows designers to realize their imaginative complex curved surfaces and sharp lines.
Lightweighting and Performance Improvement: Replacing steel with plastic reduces unsprung mass, improving handling and fuel economy.
Cost and Efficiency: Once the mold is completed, mass production costs are extremely low, and production efficiency is high.
Functional Integration: Through ingenious mold design, heat dissipation grilles, mounting points, wiring harness clips, etc., are integrated into a single part, improving assembly efficiency and reliability.
Conclusion: Motorcycle part injection molds are a combination of engineering and art. They are not only tools for mass production but also the core carrier for transforming a motorcycle's design concept, performance goals, and cost control into a real product. From a sheet of steel to exquisite plastic parts, the injection mold plays an indispensable role as both a "translator" and a "realizer."